Module "Alu1", blocks/ALU1/rtl/Alu1.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
- localparam
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| cmd | input | wire [CMD_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| co | output | wire | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
Substraction is using 2's complements.
Negating B is to find its 2's complement, 2's complement of B is ~B + 1,
that is invert and add 1.
Therefore A - B = A + B2s = A + ~B + 1.
When using RippleCarryAdder we need:
1. set carry in ci to HI for +1, ci = sub_add;
2. B' = ~B = B XOR sub_add.
References: - https://www.egr.msu.edu/classes/ece410/mason/files/Ch12.pdf
Source code:
module Alu1 #(
parameter WIDTH = 64,
localparam CMD_WIDTH = ALU1_CMD_WIDTH
)(
input wire [CMD_WIDTH-1:0] cmd,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
output wire co,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
//S012 C cmd
localparam CMD_TRANSFER = 0; // 000 0 0000 out = in1
localparam CMD_INC = 1; // 000 1 0001 out = in1 + 1
localparam CMD_ADD = 2; // 100 0 0010 out = in1 + in2
localparam CMD_ADD_PLUS1 = 3; // 100 1 0011 out = in1 + in2 + 1
localparam CMD_SUB_MINUS1 = 4; // 010 0 0100 out = in1 + ~in2
localparam CMD_SUB = 5; // 010 1 0101 out = in1 + ~in2 + 1
localparam CMD_DEC = 6; // 110 0 0110 out = in1 - 1 (in1 + 111=in1 + 000 - 1=in1 - 1)
localparam CMD_TRANSFER2 = 7; // 110 1 0111 out = in1
localparam CMD_AND = 8; // 001 1000 out = in1 & in2
localparam CMD_OR = 9; // 101 1001 out = in1 | in2
localparam CMD_XOR =10; // 011 1010 out = in1 ^ in2
localparam CMD_NOT =11; // 111 1011 out = ~in1
wire [2:0] opsel;
assign opsel[0] = (cmd == CMD_ADD || cmd == CMD_ADD_PLUS1 ||
cmd == CMD_DEC || cmd == CMD_TRANSFER2 || cmd == CMD_OR || cmd == CMD_NOT);
assign opsel[1] = cmd[2] | (cmd[3] & cmd[1]);
assign opsel[2] = cmd[3];
wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2_inv;
INV#(WIDTH) inv2_(.in(in2), .out(in2_inv));
wire [WIDTH-1:0] adder_in1;
wire [WIDTH-1:0] adder_in2;
wire [WIDTH-1:0] adder_out;
wire adder_ci;
assign adder_in1 = in1;
assign adder_ci = cmd[0];
genvar i;
generate
for (i = 0; i < WIDTH; i++) begin : in2_sel
assign adder_in2[i] = (in2[i] & opsel[0]) | (in2_inv[i] & opsel[1]);
end
endgenerate
RippleCarryAdder#(WIDTH) adder_(
.in1(adder_in1),
.in2(adder_in2),
.ci(adder_ci),
.co(co),
.sum(adder_out)
);
wire [WIDTH-1:0] logic_block_out;
MUX4#(WIDTH) logic_block_(
.in1(in1 & in2), // AND
.in2(in1 | in2), // OR
.in3(in1 ^ in2), // XOR
.in4(~in1), // NOT
.sel(opsel[1:0]),
.out(logic_block_out)
);
assign out = (opsel[2] == 1)? logic_block_out : adder_out;
endmoduleModule "AddCmp50", blocks/AddCmp/rtl/AddCmp50.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | input | wire [50-1:0] | |
| b | input | wire [50-1:0] | |
| c | input | wire [50-1:0] | |
| eq | output | wire |
Source code:
module AddCmp50 (
input wire [50-1:0] a,
input wire [50-1:0] b,
input wire [50-1:0] c,
output wire eq
);
wire [50-1:0] s;
wire [50 :0] cy;
wire [50-1:0] t;
wire group0;
wire group1;
wire group2;
wire group3;
wire group4;
wire group5;
wire group6;
wire group7;
wire group8;
wire group9;
wire group10;
wire group11;
wire group12;
assign cy[0] = 0;
FullAdder u_fa0(.in1(a[0]), .in2(b[0]), .ci(~c[0]), .sum(s[0]), .co(cy[1]));
FullAdder u_fa1(.in1(a[1]), .in2(b[1]), .ci(~c[1]), .sum(s[1]), .co(cy[2]));
FullAdder u_fa2(.in1(a[2]), .in2(b[2]), .ci(~c[2]), .sum(s[2]), .co(cy[3]));
FullAdder u_fa3(.in1(a[3]), .in2(b[3]), .ci(~c[3]), .sum(s[3]), .co(cy[4]));
FullAdder u_fa4(.in1(a[4]), .in2(b[4]), .ci(~c[4]), .sum(s[4]), .co(cy[5]));
FullAdder u_fa5(.in1(a[5]), .in2(b[5]), .ci(~c[5]), .sum(s[5]), .co(cy[6]));
FullAdder u_fa6(.in1(a[6]), .in2(b[6]), .ci(~c[6]), .sum(s[6]), .co(cy[7]));
FullAdder u_fa7(.in1(a[7]), .in2(b[7]), .ci(~c[7]), .sum(s[7]), .co(cy[8]));
FullAdder u_fa8(.in1(a[8]), .in2(b[8]), .ci(~c[8]), .sum(s[8]), .co(cy[9]));
FullAdder u_fa9(.in1(a[9]), .in2(b[9]), .ci(~c[9]), .sum(s[9]), .co(cy[10]));
FullAdder u_fa10(.in1(a[10]), .in2(b[10]), .ci(~c[10]), .sum(s[10]), .co(cy[11]));
FullAdder u_fa11(.in1(a[11]), .in2(b[11]), .ci(~c[11]), .sum(s[11]), .co(cy[12]));
FullAdder u_fa12(.in1(a[12]), .in2(b[12]), .ci(~c[12]), .sum(s[12]), .co(cy[13]));
FullAdder u_fa13(.in1(a[13]), .in2(b[13]), .ci(~c[13]), .sum(s[13]), .co(cy[14]));
FullAdder u_fa14(.in1(a[14]), .in2(b[14]), .ci(~c[14]), .sum(s[14]), .co(cy[15]));
FullAdder u_fa15(.in1(a[15]), .in2(b[15]), .ci(~c[15]), .sum(s[15]), .co(cy[16]));
FullAdder u_fa16(.in1(a[16]), .in2(b[16]), .ci(~c[16]), .sum(s[16]), .co(cy[17]));
FullAdder u_fa17(.in1(a[17]), .in2(b[17]), .ci(~c[17]), .sum(s[17]), .co(cy[18]));
FullAdder u_fa18(.in1(a[18]), .in2(b[18]), .ci(~c[18]), .sum(s[18]), .co(cy[19]));
FullAdder u_fa19(.in1(a[19]), .in2(b[19]), .ci(~c[19]), .sum(s[19]), .co(cy[20]));
FullAdder u_fa20(.in1(a[20]), .in2(b[20]), .ci(~c[20]), .sum(s[20]), .co(cy[21]));
FullAdder u_fa21(.in1(a[21]), .in2(b[21]), .ci(~c[21]), .sum(s[21]), .co(cy[22]));
FullAdder u_fa22(.in1(a[22]), .in2(b[22]), .ci(~c[22]), .sum(s[22]), .co(cy[23]));
FullAdder u_fa23(.in1(a[23]), .in2(b[23]), .ci(~c[23]), .sum(s[23]), .co(cy[24]));
FullAdder u_fa24(.in1(a[24]), .in2(b[24]), .ci(~c[24]), .sum(s[24]), .co(cy[25]));
FullAdder u_fa25(.in1(a[25]), .in2(b[25]), .ci(~c[25]), .sum(s[25]), .co(cy[26]));
FullAdder u_fa26(.in1(a[26]), .in2(b[26]), .ci(~c[26]), .sum(s[26]), .co(cy[27]));
FullAdder u_fa27(.in1(a[27]), .in2(b[27]), .ci(~c[27]), .sum(s[27]), .co(cy[28]));
FullAdder u_fa28(.in1(a[28]), .in2(b[28]), .ci(~c[28]), .sum(s[28]), .co(cy[29]));
FullAdder u_fa29(.in1(a[29]), .in2(b[29]), .ci(~c[29]), .sum(s[29]), .co(cy[30]));
FullAdder u_fa30(.in1(a[30]), .in2(b[30]), .ci(~c[30]), .sum(s[30]), .co(cy[31]));
FullAdder u_fa31(.in1(a[31]), .in2(b[31]), .ci(~c[31]), .sum(s[31]), .co(cy[32]));
FullAdder u_fa32(.in1(a[32]), .in2(b[32]), .ci(~c[32]), .sum(s[32]), .co(cy[33]));
FullAdder u_fa33(.in1(a[33]), .in2(b[33]), .ci(~c[33]), .sum(s[33]), .co(cy[34]));
FullAdder u_fa34(.in1(a[34]), .in2(b[34]), .ci(~c[34]), .sum(s[34]), .co(cy[35]));
FullAdder u_fa35(.in1(a[35]), .in2(b[35]), .ci(~c[35]), .sum(s[35]), .co(cy[36]));
FullAdder u_fa36(.in1(a[36]), .in2(b[36]), .ci(~c[36]), .sum(s[36]), .co(cy[37]));
FullAdder u_fa37(.in1(a[37]), .in2(b[37]), .ci(~c[37]), .sum(s[37]), .co(cy[38]));
FullAdder u_fa38(.in1(a[38]), .in2(b[38]), .ci(~c[38]), .sum(s[38]), .co(cy[39]));
FullAdder u_fa39(.in1(a[39]), .in2(b[39]), .ci(~c[39]), .sum(s[39]), .co(cy[40]));
FullAdder u_fa40(.in1(a[40]), .in2(b[40]), .ci(~c[40]), .sum(s[40]), .co(cy[41]));
FullAdder u_fa41(.in1(a[41]), .in2(b[41]), .ci(~c[41]), .sum(s[41]), .co(cy[42]));
FullAdder u_fa42(.in1(a[42]), .in2(b[42]), .ci(~c[42]), .sum(s[42]), .co(cy[43]));
FullAdder u_fa43(.in1(a[43]), .in2(b[43]), .ci(~c[43]), .sum(s[43]), .co(cy[44]));
FullAdder u_fa44(.in1(a[44]), .in2(b[44]), .ci(~c[44]), .sum(s[44]), .co(cy[45]));
FullAdder u_fa45(.in1(a[45]), .in2(b[45]), .ci(~c[45]), .sum(s[45]), .co(cy[46]));
FullAdder u_fa46(.in1(a[46]), .in2(b[46]), .ci(~c[46]), .sum(s[46]), .co(cy[47]));
FullAdder u_fa47(.in1(a[47]), .in2(b[47]), .ci(~c[47]), .sum(s[47]), .co(cy[48]));
FullAdder u_fa48(.in1(a[48]), .in2(b[48]), .ci(~c[48]), .sum(s[48]), .co(cy[49]));
FullAdder u_fa49(.in1(a[49]), .in2(b[49]), .ci(~c[49]), .sum(s[49]), .co(cy[50]));
assign t[0] = cy[0] ^ s[0];
assign t[1] = cy[1] ^ s[1];
assign t[2] = cy[2] ^ s[2];
assign t[3] = cy[3] ^ s[3];
assign t[4] = cy[4] ^ s[4];
assign t[5] = cy[5] ^ s[5];
assign t[6] = cy[6] ^ s[6];
assign t[7] = cy[7] ^ s[7];
assign t[8] = cy[8] ^ s[8];
assign t[9] = cy[9] ^ s[9];
assign t[10] = cy[10] ^ s[10];
assign t[11] = cy[11] ^ s[11];
assign t[12] = cy[12] ^ s[12];
assign t[13] = cy[13] ^ s[13];
assign t[14] = cy[14] ^ s[14];
assign t[15] = cy[15] ^ s[15];
assign t[16] = cy[16] ^ s[16];
assign t[17] = cy[17] ^ s[17];
assign t[18] = cy[18] ^ s[18];
assign t[19] = cy[19] ^ s[19];
assign t[20] = cy[20] ^ s[20];
assign t[21] = cy[21] ^ s[21];
assign t[22] = cy[22] ^ s[22];
assign t[23] = cy[23] ^ s[23];
assign t[24] = cy[24] ^ s[24];
assign t[25] = cy[25] ^ s[25];
assign t[26] = cy[26] ^ s[26];
assign t[27] = cy[27] ^ s[27];
assign t[28] = cy[28] ^ s[28];
assign t[29] = cy[29] ^ s[29];
assign t[30] = cy[30] ^ s[30];
assign t[31] = cy[31] ^ s[31];
assign t[32] = cy[32] ^ s[32];
assign t[33] = cy[33] ^ s[33];
assign t[34] = cy[34] ^ s[34];
assign t[35] = cy[35] ^ s[35];
assign t[36] = cy[36] ^ s[36];
assign t[37] = cy[37] ^ s[37];
assign t[38] = cy[38] ^ s[38];
assign t[39] = cy[39] ^ s[39];
assign t[40] = cy[40] ^ s[40];
assign t[41] = cy[41] ^ s[41];
assign t[42] = cy[42] ^ s[42];
assign t[43] = cy[43] ^ s[43];
assign t[44] = cy[44] ^ s[44];
assign t[45] = cy[45] ^ s[45];
assign t[46] = cy[46] ^ s[46];
assign t[47] = cy[47] ^ s[47];
assign t[48] = cy[48] ^ s[48];
assign t[49] = cy[49] ^ s[49];
assign group0 = ~(t[0] & t[1] & t[2] & t[3]);
assign group1 = ~(t[4] & t[5] & t[6] & t[7]);
assign group2 = ~(t[8] & t[9] & t[10] & t[11]);
assign group3 = ~(t[12] & t[13] & t[14] & t[15]);
assign group4 = ~(t[16] & t[17] & t[18] & t[19]);
assign group5 = ~(t[20] & t[21] & t[22] & t[23]);
assign group6 = ~(t[24] & t[25] & t[26] & t[27]);
assign group7 = ~(t[28] & t[29] & t[30] & t[31]);
assign group8 = ~(t[32] & t[33] & t[34] & t[35]);
assign group9 = ~(t[36] & t[37] & t[38] & t[39]);
assign group10 = ~(t[40] & t[41] & t[42] & t[43]);
assign group11 = ~(t[44] & t[45] & t[46] & t[47]);
assign group12 = ~(t[48] & t[49]);
assign eq = ~(group0 | group1 | group2 | group3 | group4 | group5 | group6 | group7 | group8 | group9 | group10 | group11 | group12);
endmoduleModule "BarrelShifter", blocks/BarrelShifter/rtl/BarrelShifter.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
- SHIFT_WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| shift_in_bit | input | wire | 0 for logical shift |
| shift | input | wire [SHIFT_WIDTH-1:0] | number of shifts |
| shift_rotate | input | wire | shift or rotate |
| left_right | input | wire | shift/rotate left or right |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
Barrel Shifter Author: Igor Lesik 2019-2020 Copyright: Igor Lesik 2019-2020
Source code:
module BarrelShifter #(
parameter WIDTH = 64,
parameter SHIFT_WIDTH = `CLOG2(WIDTH) // number of shift/rotate bits
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in,
input wire shift_in_bit, // 0 for logical shift
input wire [SHIFT_WIDTH-1:0] shift, // number of shifts
input wire shift_rotate, // shift or rotate
input wire left_right, // shift/rotate left or right
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
wire [WIDTH-1:0] ain; // "in" or reversed "in"
wire [WIDTH-1:0] res; // result of shifting
genvar i;
// We implement internal logic that shift/rotate LEFT.
// The direction of the final shift/rotate operation is implemented by reversing
// the input and output vector.
generate //: reverse_vectors
for (i = 0; i < WIDTH; i = i + 1)
begin: gen_reverse
MUX2#(.WIDTH(1)) mux_reverse_in_ (.in1(in[i]), .in2(in[WIDTH-1-i]), .sel(left_right), .out(ain[i]));
MUX2#(.WIDTH(1)) mux_reverse_out_ (.in1(res[i]), .in2(res[WIDTH-1-i]), .sel(left_right), .out(out[i]));
end: gen_reverse
endgenerate
// The shift/rotate (left) operation is done in stages where each stage performs
// a shift/rotate operation of a different size.
// For example, a 5 bits shift operation would result in a shift of 4 and a shift of 1
// where the stage that performs the shift of 2 would not do any shift.
// The select vector binary encoding is actually to enable the different stages of the barrel shifter.
// {stage[i+1][WIDTH-(2**i)-1:0], stage[i+1][WIDTH-1:WIDTH-(2**i)]}) when WIDTH=8:
// s3 = in 76543210
// s2 = {s3[3:0],s3[7:4]} -> 32107654
// s1 = {s2[5:0],s3[7:6]} -> 10765432
// s0 = {s1[6:0],s1[7:7]} -> 07654321
wire [WIDTH-1:0] stage[SHIFT_WIDTH:0];
assign stage[SHIFT_WIDTH] = ain;
assign res = stage[0];
generate //: stage_select
for (i = 0; i < SHIFT_WIDTH; i = i + 1)
begin: stage_mux
Mux2 #(.WIDTH(WIDTH)) mux(
.in2(stage[i+1]),
.in1({stage[i+1][WIDTH-(2**i)-1:0],
(shift_rotate)? {(2**i){shift_in_bit}} : stage[i+1][WIDTH-1:WIDTH-(2**i)]
}),
.sel(shift[i]), // i-th bit of shift
.out(stage[i]) // i-th stage either copy of prev. stage
);
end: stage_mux
endgenerate //: stage_select
endmoduleModule "Counter", blocks/Counter/rtl/Counter.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| clk | input | wire | |
| rst_n | input | wire | |
| load | input | wire | |
| in | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| up_down | input | wire | |
| count_en | input | wire | |
| out | output | reg [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| co | output | reg |
Source code:
module Counter #(
parameter WIDTH=8
)(
input wire clk,
input wire rst_n,
input wire load,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in,
input wire up_down,
input wire count_en,
output reg [WIDTH-1:0] out,
output reg co
);
localparam WIDTH_WITH_CARRY = WIDTH + 1;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if (!rst_n) begin // sync reset
{co,out} <= {WIDTH_WITH_CARRY{1'b0}};
end else if (load) begin // sync load
{co,out} <= in;
end else if (count_en) begin // sync increment/decrement
if (up_down)
{co,out} <= out + 1'b1;
else
{co,out} <= out - 1'b1;
end
end
endmoduleModule "Decoder", blocks/Decoder/rtl/Decoder.sv
Parameters:
- SIZE
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [SIZE-1:0] | |
| en | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
i[j] - take j-th bit of number i For example, for 3-8 decoder: If in is 5(101), 5[0]=1, 5[1]=0, 5[2]=1 for i [0..7] i=5=b101, 5[0]=1, 5[1]=0, 5[2]=1 out[5]=5[0] & !5[1] & !5[2] = 1 & !0 & 1 = 1
i=6=b110, 6[0]=0, 6[1]=1, 6[2]=1
out[6]=!5[0] & 5[1] & 5[2] = !1 & 0 & 1 = 0 & 0 & 1 = 0
Source code:
module Decoder #(
parameter SIZE = 3,
parameter WIDTH = 1 << SIZE
)(
input wire [SIZE-1:0] in,
input wire en,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
/*
always @* begin
out = {WIDTH{1'b0}};
out[in] = 1'b1;
end
*/
wire [SIZE-1:0] nin;
assign nin = ~in;
genvar i, j;
generate
for (i = 0; i < WIDTH; i = i + 1) begin
wire [SIZE-1:0] sel;
for (j = 0; j < SIZE; j = j + 1) begin
assign sel[j] = i[j] ? in[j] : nin[j];
end
assign out[i] = en & ( &sel );
end
endgenerate
endmoduleModule "Encoder8_3", blocks/Encoder/rtl/Encoder8_3.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [8-1:0] | |
| out | output | wire [3-1:0] | |
| d | input | [WIDTH-1:0] |
Source code:
module Encoder8_3(
input wire [8-1:0] in,
output wire [3-1:0] out
);
localparam SIZE = 3;
localparam WIDTH = 1 << SIZE;
assign out = enc(in);
function [SIZE-1:0] enc(input [WIDTH-1:0] d);
casex (d)
8'b1xxxxxxx: enc = 3'd7;
8'b01xxxxxx: enc = 3'd6;
8'b001xxxxx: enc = 3'd5;
8'b0001xxxx: enc = 3'd4;
8'b00001xxx: enc = 3'd3;
8'b000001xx: enc = 3'd2;
8'b0000001x: enc = 3'd1;
default: enc = 3'd0;
endcase
endfunction
endmoduleModule "Incr16", blocks/Incr/rtl/Incr16.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [15:0] | |
| out | output | wire [15:0] | |
| cy | output | wire |
16-bit Incrementor.
Source code:
module Incr16 (
input wire [15:0] in,
output wire [15:0] out,
output wire cy
);
wire [ 3: 0] all1_3_0;
wire [ 7: 4] all1_7_4;
wire [11: 8] all1_11_8;
wire [15:12] all1_15_12;
wire [ 3: 0] incr_3_0;
wire [ 7: 4] incr_7_4;
wire [11: 8] incr_11_8;
wire [15:12] incr_15_12;
assign all1_3_0 = ~(in[ 3] & in[ 2] & in[ 1] & in[ 0]);
assign all1_7_4 = ~(in[ 7] & in[ 6] & in[ 5] & in[ 4]);
assign all1_11_8 = ~(in[11] & in[10] & in[ 9] & in[ 8]);
assign all1_15_12 = ~(in[15] & in[14] & in[13] & in[12]);
Incr4 u_incr_3_0 (.in(in[ 3: 0]), .out(incr_3_0));
Incr4 u_incr_7_4 (.in(in[ 7: 4]), .out(incr_7_4));
Incr4 u_incr_11_8 (.in(in[11: 8]), .out(incr_11_8));
Incr4 u_incr_15_12(.in(in[15:12]), .out(incr_15_12));
assign out[ 3: 0] = incr_3_0;
assign out[ 7: 4] = ~all1_3_0 ? incr_7_4 : in[7:4];
assign out[11: 8] = ~(all1_3_0 | all1_7_4) ? incr_11_8 : in[11:8];
assign out[15:12] = ~(all1_3_0 | all1_7_4 | all1_11_8) ? incr_15_12 : in[15:12];
assign cy = ~(all1_3_0 | all1_7_4 | all1_11_8 | all1_15_12);
endmoduleModule "Incr3", blocks/Incr/rtl/Incr3.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [2:0] | |
| out | output | wire [2:0] |
3-bit Incrementor block to be used in building Nx3 Fast Incrementor.
Source code:
module Incr3 (
input wire [2:0] in,
output wire [2:0] out
);
assign out[0] = ~in[0];
assign out[1] = ~(~( in[0] & ~in[1]) &
~(~in[0] & in[1]));
assign out[2] = ~(~( in[0] & in[1] & ~in[2]) &
~( ~in[1] & in[2]) &
~(~in[0] & in[1] & in[2]));
endmoduleModule "Incr4", blocks/Incr/rtl/Incr4.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [3:0] | |
| out | output | wire [3:0] |
4-bit Incrementor.
Source code:
module Incr4 (
input wire [3:0] in,
output wire [3:0] out
);
assign out[0] = ~in[0];
assign out[1] = ~(~( in[0] & ~in[1]) &
~(~in[0] & in[1]));
assign out[2] = ~(~( in[0] & in[1] & ~in[2]) &
~( ~in[1] & in[2]) &
~(~in[0] & in[1] & in[2]));
assign out[3] = ~(~( in[0] & in[1] & in[2] & ~in[3]) &
~( ~in[2] & in[3]) &
~( ~in[1] & in[2] & in[3]) &
~(~in[0] & in[1] & in[2] & in[3]));
endmoduleModule "Incr9", blocks/Incr/rtl/Incr9.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [8:0] | |
| out | output | wire [8:0] | |
| cy | output | wire |
9-bit Fast Incrementor
Source code:
module Incr9 (
input wire [8:0] in,
output wire [8:0] out,
output wire cy
);
wire [2:0] nand_2_0;
wire [5:3] nand_5_3;
wire [8:6] nand_8_6;
wire all1_2_0;
wire all1_5_0;
wire [2:0] incr_5_3;
wire [2:0] incr_8_6;
assign nand_2_0 = ~(in[0] & in[1] & in[2]);
assign nand_5_3 = ~(in[3] & in[4] & in[5]);
assign nand_8_6 = ~(in[6] & in[7] & in[8]);
assign all1_2_0 = ~nand_2_0;
assign all1_5_0 = ~(nand_2_0 | nand_5_3);
assign cy = ~(nand_2_0 | nand_5_3 | nand_8_6);
Incr3 u_incr3_2_0(.in(in[2:0]), .out(out[2:0]));
Incr3 u_incr3_5_3(.in(in[5:3]), .out(incr_5_3));
Incr3 u_incr3_8_6(.in(in[8:6]), .out(incr_8_6));
assign out[5:3] = all1_2_0 ? incr_5_3 : in[5:3];
assign out[8:6] = all1_5_0 ? incr_8_6 : in[8:6];
endmoduleModule "CoreDbgApb", blocks/JtagCoreDbg/rtl/CoreDbgApb.sv
Parameters:
- APB_ADDR_WIDTH
- APB_WDATA_WIDTH
- APB_RDATA_WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| clk | input | wire | rising edge of `clk` times all transfers on the APB |
| rst_n | input | wire | Signals from APB Master and APB bus |
| addr | input | wire [APB_ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| sel | input | wire | slave is selected and data transfer is required |
| enable | input | wire | indicates the second+ cycles of an APB transfer |
| wr_rd | input | wire | direction=HIGH? wr:rd |
| wdata | input | wire [APB_WDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | driven by Bridge when wr_rd=HIGH |
| wstrobe | input | wire [3:0] | Signals driven by current Slave |
| ready | output | reg | slave uses this signal to extend an APB transfer, when ready is LOW the transfer extended |
| rdata | output | reg [APB_RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | not implemented slave_err |
| core_dbg_req | output | reg | |
| core_dbg_wr_rd | output | reg | Debug register write/read request |
| core_dbg_addr | output | reg [APB_ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] | Debug register address |
| core_dbg_wdata | output | reg [APB_WDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | Debug register write data |
| core_dbg_rdata | input | wire [APB_RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| core_dbg_rd_ready | input | wire |
Core Debug APB bus interface.
Authors: Igor Lesik 2020
Module CoreDbgApb is APB bus slave.
Source code:
module CoreDbgApb #(
parameter APB_ADDR_WIDTH =5,
parameter APB_WDATA_WIDTH=32,
parameter APB_RDATA_WIDTH=32
)(
input wire clk, // rising edge of `clk` times all transfers on the APB
input wire rst_n,
// Signals from APB Master and APB bus
input wire [APB_ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] addr,
input wire sel, // slave is selected and data transfer is required
input wire enable, // indicates the second+ cycles of an APB transfer
input wire wr_rd, // direction=HIGH? wr:rd
input wire [APB_WDATA_WIDTH-1:0] wdata, // driven by Bridge when wr_rd=HIGH
input wire [3:0] wstrobe, // which byte lanes to update during a write transfer wdata[(8n + 7):(8n)]
// Signals driven by current Slave
output reg ready, // slave uses this signal to extend an APB transfer, when ready is LOW the transfer extended
output reg [APB_RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] rdata,
// not implemented slave_err
output reg core_dbg_req,
output reg core_dbg_wr_rd, // Debug register write/read request
output reg [APB_ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] core_dbg_addr, // Debug register address
output reg [APB_WDATA_WIDTH-1:0] core_dbg_wdata, // Debug register write data
input wire [APB_RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] core_dbg_rdata,
input wire core_dbg_rd_ready
);
reg [1:0] state;
localparam [1:0] IDLE=0, WRITE=1, READ=2, READ_READY=3;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if (!rst_n) begin
state <= IDLE;
core_dbg_req <= 0;
ready <= 1;
end else begin
case (state)
IDLE: begin
//if (sel) $display("%t Core Dbg Apb Slave selected", $time);
state <= sel? (wr_rd? WRITE:READ) : IDLE;
core_dbg_req <= sel;
core_dbg_wr_rd <= wr_rd;
core_dbg_addr <= addr;
core_dbg_wdata <= wdata;
rdata <= 32'h0000_0000; //FIXME
ready <= ~sel | (sel & wr_rd) ;
end
WRITE: begin
if (sel && wr_rd) begin // sel and other inputs MUST be stable at least 2 cycles
core_dbg_req <= 0;
core_dbg_wr_rd <= 1;
core_dbg_addr <= addr;
core_dbg_wdata <= wdata;
ready <= 1;
//$display("%t Core Dbg Apb write[%h]=%h", $time, addr, wdata);
end
state <= IDLE;
end
READ: begin
//if (sel && !wr_rd) begin // sel and other inputs MUST be stable at least 2 cycles
core_dbg_req <= 0;
core_dbg_wr_rd <= 0;
core_dbg_addr <= addr;
rdata <= core_dbg_rdata;
ready <= core_dbg_rd_ready;
if (core_dbg_rd_ready) begin
state <= READ_READY;
$display("%t CoreDbgApb: read[%h]=%h", $time, addr, core_dbg_rdata);
end else begin
state <= READ;
end
//end
end
READ_READY: begin
state <= IDLE;
ready <= 1;
core_dbg_req <= 0;
end
default: begin
state <= IDLE;
core_dbg_req <= 0;
ready <= 1;
end
endcase
end
end
endmoduleModule "CoreDbgPort", blocks/JtagCoreDbg/rtl/CoreDbgPort.sv
Parameters:
- MEMI_NR_SLAVES
- MEMI_ADDR_WIDTH
- MEMI_WDATA_WIDTH
- MEMI_RDATA_WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| tck | input | wire | test clock |
| trst | input | wire | test reset |
| tdi | input | wire | test Data In |
| tms | input | wire | test Mode Select |
| insn_jdpacc_select | input | wire | IR==JDPACC |
| insn_cdpacc_select | input | wire | IR==CDPACC |
| state_test_logic_reset | input | wire | TAP_STATE==TEST_LOGIC_REST |
| state_capture_dr | input | wire | TAP_STATE==CAPTURE_DR |
| state_shift_dr | input | wire | TAP_STATE==SHIFT_DR |
| state_update_dr | input | wire | TAP_STATE==UPDATE_DR |
| jdpacc_tdo | output | reg | JDPACC DR output |
| cdpacc_tdo | output | reg | CDPACC DR output |
| memi_clk | input | wire | |
| memi_rst | input | wire | |
| memi_addr | output | reg [MEMI_ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| memi_sel | output | reg [MEMI_NR_SLAVES-1:0] | slave selected & data transfer required |
| memi_wr_rd | output | reg | direction=HIGH? wr:rd |
| memi_wdata | output | reg [MEMI_WDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| memi_rdata | input | wire [MEMI_RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| memi_ready | input | wire | |
| jdpacc | input | [WIDTH-1:0] |
Core Debug Port (CDP).
Authors: Igor Lesik 2021
Core Debug Port makes the communation channel between JTAG and Core Debug logic.
CDP has two interfaces:
- JTAG interface and
- memory bus interface to Core Debug logic.
The debugger uses the JTAG interface to execute instructions JDPACC, CDPACC by going through the TAP state machine, then the instructions take the data and load it into the JDPACC, CDPACC registers, and depending on the data, different registers within the JDP or CDP are accessed, providing the desired comminication to the Core Debug logic.
In the Capture-DR state, the result of the previous transaction, if any, is returned, together with a 4-bit ACK response.
In the Shift-DR state, ACK[3:0] is shifted out first, then 32 bits
of "Read Result" data is shifted out.
As the returned data is shifted out to TDO,
new data is shifted in from TDI.
Update-DR operation fulfills the read or write request that is formed by the values that were shifted into the scan chain.
Source code:
module CoreDbgPort #(
parameter MEMI_NR_SLAVES = 1,
parameter MEMI_ADDR_WIDTH = 5,
parameter MEMI_WDATA_WIDTH = 32,
parameter MEMI_RDATA_WIDTH = 32
)(
input wire tck, // test clock
input wire trst, // test reset
input wire tdi, // test Data In
input wire tms, // test Mode Select
input wire insn_jdpacc_select, // IR==JDPACC
input wire insn_cdpacc_select, // IR==CDPACC
input wire state_test_logic_reset, // TAP_STATE==TEST_LOGIC_REST
input wire state_capture_dr, // TAP_STATE==CAPTURE_DR
input wire state_shift_dr, // TAP_STATE==SHIFT_DR
input wire state_update_dr, // TAP_STATE==UPDATE_DR
output reg jdpacc_tdo, // JDPACC DR output
output reg cdpacc_tdo, // CDPACC DR output
input wire memi_clk,
input wire memi_rst,
output reg [MEMI_ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] memi_addr,
output reg [MEMI_NR_SLAVES-1:0] memi_sel, // slave selected & data transfer required
output reg memi_wr_rd, // direction=HIGH? wr:rd
output reg [MEMI_WDATA_WIDTH-1:0] memi_wdata,
input wire [MEMI_RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] memi_rdata,
input wire memi_ready
);
localparam WIDTH = 32+4;
reg [WIDTH-1:0] jdpacc_reg;
reg [WIDTH-1:0] cdpacc_reg;
assign jdpacc_tdo = jdpacc_reg[0];
assign cdpacc_tdo = cdpacc_reg[0];
localparam JDPACC_ID = 36'h0;
always @(posedge tck)
begin
if (trst == 1)
jdpacc_reg <= JDPACC_ID;
else if (state_test_logic_reset)
jdpacc_reg <= JDPACC_ID;
else if (insn_jdpacc_select & state_shift_dr)
jdpacc_reg <= {tdi, jdpacc_reg[WIDTH-1:1]};
else if (insn_jdpacc_select & state_capture_dr)
jdpacc_reg <= jdpacc_capture_dr();
else if (insn_jdpacc_select & state_update_dr)
jdpacc_reg <= jdpacc_update_dr(jdpacc_reg);
end
function [WIDTH-1:0] jdpacc_capture_dr();
jdpacc_capture_dr = 'h0;
endfunction
function [WIDTH-1:0] jdpacc_update_dr(input [WIDTH-1:0] jdpacc);
jdpacc_update_dr = jdpacc;
endfunction
localparam CDP_OP_SELECT = 3'b000,
CDP_OP_TADDR = 3'b001,
CDP_OP_DTR = 3'b010;
reg cdp_req, cdp_update, cdp_cmd_wr, cdp_cmd_rd;
reg [2:0] cdp_cmd_op;
reg [31:0] cdp_cmd_data;
always_ff @(posedge tck)
begin
if (trst == 1) begin
cdpacc_reg <= 'h0;
cdp_req <= 0;
cdp_update <= 0;
end else if (state_test_logic_reset) begin
cdpacc_reg <= 'h0;
cdp_req <= 0;
cdp_update <= 0;
end else if (insn_cdpacc_select & state_shift_dr) begin
//$display("%t CDPACC shift-in %b", $time, {tdi, cdpacc_reg[WIDTH-1:1]});
cdpacc_reg <= {tdi, cdpacc_reg[WIDTH-1:1]};
cdp_req <= 0;
cdp_update <= 0;
end else if (insn_cdpacc_select & state_capture_dr) begin
//$display("%t captured CDPACC=%h", $time, cdpacc_capture_dr());
cdpacc_reg <= cdpacc_capture_dr();
cdp_req <= 0;
cdp_update <= 0;
end else if (insn_cdpacc_select & state_update_dr) begin
// **Update-DR** operation fulfills the read or write request that is
// formed by the values that were shifted into the scan chain.
cdp_update <= 1;
cdpacc_reg <= cdpacc_reg;
cdp_req <= (cdpacc_reg[3:1] == CDP_OP_DTR);
cdp_cmd_wr <= cdpacc_reg[0];
cdp_cmd_rd <= ~cdpacc_reg[0];
cdp_cmd_op <= cdpacc_reg[3:1];
cdp_cmd_data <= cdpacc_reg[35:4];
$display("%t CDP Update-DR wr=%b op=%b data=%h", $time,
cdpacc_reg[0], cdpacc_reg[3:1], cdpacc_reg[35:4]);
end else begin
cdp_req <= 0;
cdp_update <= 0;
end
end
// cdp_req synchronized to Memory Interface clock
reg memi_req;
reg memi_req_d1; // signals MUST be stable for 2 clocks on APB
Jtag2MemiSync _jtag2memi_sync(
.src_clk(tck), // Source domain slow clock
.src_rst(trst), // Source domain reset
.src_req(cdp_req), // Source domain signal to be synchronized
.dst_clk(memi_clk), // Destination domain fast clock
.dst_rst(memi_rst), // Destination domain reset
.dst_req(memi_req) // Destination domain signal that follows src_req
);
reg [31:0] cdpacc_result;
reg [ 3:0] cdpacc_ack;
// In the **Capture-DR** state, the result of the previous transaction,
// if any, is returned, together with a 4-bit ACK response.
//
function [WIDTH-1:0] cdpacc_capture_dr();
cdpacc_capture_dr = {cdpacc_result, cdpacc_ack};
endfunction
reg [31:0] cdp_dr_select, cdp_dr_taddr, cdp_dr_dtr;
always @(posedge tck)
begin
if (cdp_update) begin
case (cdp_cmd_op)
CDP_OP_SELECT: cdp_dr_select <= cdp_cmd_data;
CDP_OP_TADDR: cdp_dr_taddr <= cdp_cmd_data;
CDP_OP_DTR: cdp_dr_dtr <= cdp_cmd_data;
default: begin end
endcase
case (cdp_cmd_op)
CDP_OP_SELECT: $display("%t CDP select core %d", $time, cdp_cmd_data);
CDP_OP_TADDR: $display("%t CDP select addr %h", $time, cdp_cmd_data);
CDP_OP_DTR: $display("%t CDP write DTR %h", $time, cdp_cmd_data);
endcase
end
end
reg memi_wait_rd_reply;
// APB transaction starts when one-hot bit of `memi_sel` is HIGH.
//
always_ff @(posedge memi_clk)
begin
if (memi_rst) begin
memi_sel <= 'h0;
memi_req_d1 <= 0;
end else if (memi_req) begin
$display("%t MEMI REQ WR/RD=%b addr=%h data=%h",
$time, cdp_cmd_wr, cdp_dr_taddr, cdp_dr_dtr);
memi_sel <= 1;// FIXME TODO decode cdp_dr_select;
memi_addr <= cdp_dr_taddr;
memi_wdata <= cdp_dr_dtr;
memi_wr_rd <= cdp_cmd_wr;
memi_req_d1 <= 1;
end else if (memi_req_d1) begin
memi_req_d1 <= 0;
memi_sel <= memi_sel;
memi_addr <= memi_addr;
memi_wdata <= memi_wdata;
memi_wr_rd <= memi_wr_rd;
end else begin
memi_sel <= memi_wait_rd_reply & ~memi_ready;
memi_addr <= 'h0;
memi_wdata <= 'h0;
memi_wr_rd <= 0;
memi_req_d1 <= 0;
end
end
always_ff @(posedge memi_clk)
begin
if (memi_rst) begin
memi_wait_rd_reply <= 0;
end else begin
if (memi_wait_rd_reply) begin
memi_wait_rd_reply <= ~memi_ready;
if (memi_ready) begin
$display("%t CDP: APB read reply %h", $time, memi_rdata);
cdpacc_result <= memi_rdata; // TODO fast-slow clock sync?
cdpacc_ack <= 4'b0000;
end else begin
$display("%t CDP: waiting for APB ready HIGH", $time);
end
end else begin
memi_wait_rd_reply <= memi_sel & ~memi_wr_rd;
if (memi_sel & ~memi_wr_rd)
$display("%t CDP: Enter wait-rd-reply state", $time);
end
end
end
endmoduleModule "DbgAccPort", blocks/JtagCoreDbg/rtl/DbgAccPort.sv
Parameters:
- MEMI_NR_SLAVES
- MEMI_ADDR_WIDTH
- MEMI_WDATA_WIDTH
- MEMI_RDATA_WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| tck | input | wire | test clock |
| trst | input | wire | test reset |
| tdi | input | wire | test Data In |
| tms | input | wire | test Mode Select |
| tdo | output | reg | test Data Out |
| memi_clk | input | wire | |
| memi_rst | input | wire | |
| memi_addr | output | reg [MEMI_ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| memi_sel | output | reg [MEMI_NR_SLAVES-1:0] | |
| memi_wr_rd | output | reg | |
| memi_wdata | output | reg [MEMI_WDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| memi_rdata | input | wire [MEMI_RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| memi_ready | input | wire |
Debug Access Port (DAP).
Author: Igor Lesik 2021
Debug Access Port (DAP) is an implementation of Debug Interface. DAP provides external debugger with a standard interface to access Core debug facilities.
DAP contains:
- JTAG TAP Controller with TAP FSM.
- JTAG Debug Port and Core Debug Port.
Source code:
module DbgAccPort #(
parameter MEMI_NR_SLAVES=1,
parameter MEMI_ADDR_WIDTH=5,
parameter MEMI_WDATA_WIDTH=32,
parameter MEMI_RDATA_WIDTH=32
)(
input wire tck, // test clock
input wire trst, // test reset
input wire tdi, // test Data In
input wire tms, // test Mode Select
output reg tdo, // test Data Out
input wire memi_clk,
input wire memi_rst,
output reg [MEMI_ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] memi_addr,
output reg [MEMI_NR_SLAVES-1:0] memi_sel,
output reg memi_wr_rd,
output reg [MEMI_WDATA_WIDTH-1:0] memi_wdata,
input wire [MEMI_RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] memi_rdata,
input wire memi_ready
);
wire jdpacc_tdo;
wire cdpacc_tdo;
wire insn_jdpacc_select;
wire insn_cdpacc_select;
wire state_test_logic_reset;
wire state_capture_dr;
wire state_shift_dr;
wire state_update_dr;
JtagTap _jtag_tap(
.tck(tck),
.trst(trst),
.tdi(tdi),
.tms(tms),
.tdo(tdo),
.jdpacc_tdo(jdpacc_tdo),
.cdpacc_tdo(cdpacc_tdo),
.state_test_logic_reset,
.state_capture_dr,
.state_shift_dr,
.state_update_dr,
.insn_cdpacc_select
);
CoreDbgPort _cdp(
.tck(tck),
.trst(trst),
.tdi(tdi),
.tms(tms),
.insn_jdpacc_select(insn_jdpacc_select),
.insn_cdpacc_select(insn_cdpacc_select),
.state_test_logic_reset,
.state_capture_dr,
.state_shift_dr,
.state_update_dr,
.jdpacc_tdo(jdpacc_tdo),
.cdpacc_tdo(cdpacc_tdo),
.memi_clk,
.memi_rst,
.memi_addr,
.memi_sel,
.memi_wr_rd,
.memi_wdata,
.memi_rdata,
.memi_ready
);
endmoduleModule "DbgApbBus", blocks/JtagCoreDbg/rtl/DbgApbBus.sv
Parameters:
- ADDR_WIDTH
- WDATA_WIDTH
- RDATA_WIDTH
- NR_SLAVES
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| clk | input | wire | rising edge of `clk` times all transfers on the APB |
| rst_n | input | wire | Signals driven by APB bridge |
| addr | input | wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| sel | input | wire [NR_SLAVES-1:0] | slave is selected and data transfer is required |
| enable | output | reg | indicates the second+ cycles of an APB transfer |
| wr_rd | input | wire | direction=HIGH? wr:rd |
| wdata | input | wire [WDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | driven by Bridge when wr_rd=HIGH |
| wstrobe | input | wire [3:0] | Signals driven by current Slave |
| ready | output | reg | slave uses this signal to extend an APB transfer |
| rdata | output | reg [RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | Signals driven by Slaves |
| s2m_ready | input | wire [NR_SLAVES-1:0] | |
| s2m_data | input | wire [RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| NR_SLAVES | input | wire [RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] |
APB bus.
Author: Igor Lesik 2020
The Advanced Peripheral Bus (APB) is used for connecting low bandwidth peripherals. It is a simple non-pipelined protocol that can be used to read/write from a master to a number of slaves through the shared bus. The reads and writes shares the same set of signals and no burst data transfers are supported. APB is a simple interface that could be used to provide access to the programmable control registers of peripheral devices.
Unpipelined protocol means that a second transfer cannot start before the first transfer completes. Every transfer takes at least two cycles.
Master/APB Bridge
^
|
v
bus ------------------------------
^ ^ ^
| | |
v v v
slave1 slave2 slave3
Programming the control registers of internal CPU devices, for example, Debug Logic control registers can be implemented with JTAG TAP connected to APB.
TDI ----->| R/W | Address | DATA |-----> TDO
| | |
| | +--->
| +-----------> APB transaction
+------------------->
The APB protocol has two independent data buses, one for read data and one for write data. Because the buses do not have their own individual handshake signals, it is not possible for data transfers to occur on both buses at the same time.
Verilog module ApbBus takes inputs from APB Bridge and outputs Slave signals to APB Bridge.
Source code:
module DbgApbBus #(
parameter ADDR_WIDTH=32,
parameter WDATA_WIDTH=32,
parameter RDATA_WIDTH=32,
parameter NR_SLAVES=1
)(
input wire clk, // rising edge of `clk` times all transfers on the APB
input wire rst_n,
// Signals driven by APB bridge
input wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] addr,
input wire [NR_SLAVES-1:0] sel, // slave is selected and data transfer is required
output reg enable, // indicates the second+ cycles of an APB transfer
input wire wr_rd, // direction=HIGH? wr:rd
input wire [WDATA_WIDTH-1:0] wdata, // driven by Bridge when wr_rd=HIGH
input wire [3:0] wstrobe, // which byte lanes to update during a write transfer wdata[(8n + 7):(8n)]
// Signals driven by current Slave
output reg ready, // slave uses this signal to extend an APB transfer
output reg [RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] rdata,
// not implemented slave_err
// Signals driven by Slaves
input wire [NR_SLAVES-1:0] s2m_ready,
input wire [RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] s2m_data[NR_SLAVES]
);
genvar i;
// ====================================================================
// Mux all s2m signals based on currently selected Slave using OR gates.
// ====================================================================
wire [NR_SLAVES-1:0] sel_s2m_ready; // AND2(sel[n], s2m_ready[n])
wire [RDATA_WIDTH-1:0] sel_s2m_data[NR_SLAVES];
generate
for (i = 0; i < NR_SLAVES; i = i + 1) begin
assign sel_s2m_ready[i] = sel[i] & s2m_ready[i];
assign sel_s2m_data[i] = {RDATA_WIDTH{sel[i]}} & s2m_data[i];
end
endgenerate
assign ready = |sel_s2m_ready;
always_comb
begin
rdata = {RDATA_WIDTH{1'b0}};
for (int unsigned slave_id = 0; slave_id < NR_SLAVES; slave_id++)
begin
rdata |= sel_s2m_data[slave_id];
end
end
// =========================
// APB bus state transitions
// =========================
wire transfer_required;
assign transfer_required = |sel; // start transfer if some Slave is selected
reg [1:0] state;
localparam [1:0] IDLE=0, SETUP=1, ACCESS=2, ILLEGAL_STATE=3;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if (!rst_n) begin
state <= IDLE;
end else begin
case (state)
IDLE: begin
state <= transfer_required? SETUP:IDLE;
end
SETUP: begin
// The bus only remains in the SETUP state for one clock cycle
// and always moves to the ACCESS state on the next
// rising edge of the clock.
state <= ACCESS;
end
ACCESS: begin
// Exit from the ACCESS state is controlled by the READY signal from the slave:
// - If READY is held LOW by the slave then the peripheral bus remains in
// the ACCESS state.
// - If READY is driven HIGH by the slave then the ACCESS state is exited
// and the bus returns to the IDLE state if no more transfers are required.
// Alternatively, the bus moves directly to the SETUP state if another transfer follows.
state <= ready? (transfer_required? SETUP:IDLE) : ACCESS;
end
ILLEGAL_STATE: begin
state <= IDLE;
end
endcase
end
end
// The enable signal, ENABLE, is asserted in the ACCESS state.
assign enable = (state == ACCESS);
endmoduleModule "Jtag2MemiSync", blocks/JtagCoreDbg/rtl/Jtag2MemiSync.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| src_clk | input | wire | slow Source domain clock |
| src_rst | input | wire | Source domain reset |
| src_req | input | wire | Source domain signal to be synchronized |
| dst_clk | input | wire | fast Destination domain clock |
| dst_rst | input | wire | Destination domain reset |
| dst_req | output | reg | Destination domain signal that follows src_req |
Slow JTAG to fast Memory Interface clock domain synchronization.
Author: Igor Lesik 2021
Toggle synchronizer is used to synchronize a pulse generating
in source clock domain to destination clock domain.
Signal cdp_req is a pulse because state_capture_dr is HIGH for 1 cycle.
First, stretch source impulse.


Next, a circuit in the destination clock domain to convert the toggle back into a pulse.


References:
- https://www.edn.com/get-those-clock-domains-in-sync/
- https://www.edn.com/synchronizer-techniques-for-multi-clock-domain-socs-fpgas/
- https://www.verilogpro.com/clock-domain-crossing-part-2/
Source code:
module Jtag2MemiSync (
input wire src_clk, // slow Source domain clock
input wire src_rst, // Source domain reset
input wire src_req, // Source domain signal to be synchronized
input wire dst_clk, // fast Destination domain clock
input wire dst_rst, // Destination domain reset
output reg dst_req // Destination domain signal that follows src_req
);
reg src_toggle;
always_ff @(posedge src_clk)
begin
if (src_rst)
src_toggle <= 1'b0;
else if (src_req)
src_toggle <= ~src_toggle;
end
// 2FF Synchronizer
reg q1, q2;
always_ff @(posedge dst_clk) begin
if (dst_rst)
q1 <= 1'b0;
else
q1 <= src_toggle;
end
always_ff @(posedge dst_clk) begin
if (dst_rst)
q2 <= 1'b0;
else
q2 <= q1;
end
// Convert toggle back to pulse
reg q3;
always_ff @(posedge dst_clk) begin
if (dst_rst)
q3 <= 1'b0;
else
q3 <= q2;
end
assign dst_req = q3 ^ q2;
endmoduleModule "JtagTap", blocks/JtagCoreDbg/rtl/JtagTap.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| tck | input | wire | test clock |
| trst | input | wire | test reset |
| tdi | input | wire | test Data In |
| tms | input | wire | test Mode Select |
| tdo | output | reg | test Data Out |
| jdpacc_tdo | input | wire | |
| cdpacc_tdo | input | wire | |
| state_test_logic_reset | output | reg | |
| state_capture_dr | output | reg | |
| state_shift_dr | output | reg | |
| state_update_dr | output | reg | |
| insn_cdpacc_select | output | reg |
JTAG device TAP.
Author: Igor Lesik 2020
In JTAG, devices expose one or more test access ports (TAPs). A daisy chain of TAPs is called a scan chain.
The TAP connector pins are:
- TDI: Test Data In
- TDO: Test Data Out
- TCK: Test Clock
- TMS: Test Mode Select
- TRST: Test Reset (optional)
To use JTAG, a host is connected to the target's JTAG signals (TMS, TCK, TDI, TDO, etc.) through some kind of JTAG adapter, which may need to handle issues like level shifting and galvanic isolation. The adapter connects to the host using some interface such as USB, PCI, Ethernet, and so forth.
The host communicates with the TAPs by manipulating TMS and TDI in conjunction with TCK, and reading results through TDO.
TMS/TDI/TCK transitions create the basic JTAG communication primitive on which higher layer protocols build.
The test access point (TAP) is composed of:
- the TAP controller,
- an instruction register,
- and several test data registers,
- in addition to some glue-logic.
The TAP controller contains the testing state machine, and is responsible for interpreting the TCK and TMS signals.
The data input pin is used for loading data into the boundary cells between physical pins and the IC core, and loading data into the instruction register or one of the data registers.
The data output pin is used to read data from the boundary cells, or to read data from the instruction or data registers.
References:
- IEEE 1149.1-1990 - IEEE Standard Test Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architecture
- Timeline of JTAG-related standards
- JTAG connectors and interfaces
- practical example of JTAG interface programming with Black Magic Probe
- JTAG Primer from TI
- Boundary-scan test example
- Adding User Specific Registers to JTAG
Source code:
module JtagTap #(
localparam INSN_WIDTH=8,
localparam STATE_WIDTH=4
)(
input wire tck, // test clock
input wire trst, // test reset
input wire tdi, // test Data In
input wire tms, // test Mode Select
output reg tdo, // test Data Out
input wire jdpacc_tdo,
input wire cdpacc_tdo,
output reg state_test_logic_reset,
output reg state_capture_dr,
output reg state_shift_dr,
output reg state_update_dr,
output reg insn_cdpacc_select
);
wire insn_tdo; // TAP InsnReg TDO wire
wire debug_tdo;
wire bs_chain_tdo;
wire mbist_tdo;
//wire state_test_logic_reset;
//wire state_capture_dr;
wire state_capture_ir;
//wire state_shift_dr;
wire state_shift_ir;
wire state_update_ir;
wire state_pause_ir;
wire state_pause_dr;
wire state_exit1_ir, state_exit2_ir;
wire state_exit1_dr, state_exit2_dr;
wire state_run_test_idle, state_select_dr_scan;
wire insn_extest_select;
wire insn_sample_preload_select;
wire insn_idcode_select;
wire insn_mbist_select;
wire insn_debug_select;
wire insn_bypass_select;
wire insn_jdpacc_select;
//wire insn_cdpacc_select;
wire [INSN_WIDTH-1:0] latched_jtag_ir;
wire [STATE_WIDTH-1:0] state;
JtagTapFsm _fsm(
.tck(tck),
.trst(trst),
.tms(tms),
.state(state),
.tms_reset(tms_reset), // 5 consecutive TMS=1 causes reset
.state_test_logic_reset(state_test_logic_reset),
.state_run_test_idle(state_run_test_idle),
.state_select_dr_scan(state_select_dr_scan),
.state_capture_dr(state_capture_dr),
.state_shift_dr(state_shift_dr),
.state_exit1_dr(state_exit1_dr),
.state_pause_dr(state_pause_dr),
.state_exit2_dr(state_exit2_dr),
.state_update_dr(state_update_dr),
.state_select_ir_scan(state_select_ir_scan),
.state_capture_ir(state_capture_ir),
.state_shift_ir(state_shift_ir),
.state_exit1_ir(state_exit1_ir),
.state_pause_ir(state_pause_ir),
.state_exit2_ir(state_exit2_ir),
.state_update_ir(state_update_ir)
);
JtagTapInsnReg _insn_reg(
.tck(tck),
.trst(trst),
.tdi(tdi),
.insn_tdo(insn_tdo),
.state_test_logic_reset(state_test_logic_reset),
.state_capture_ir(state_capture_ir),
.state_shift_ir(state_shift_ir),
.state_update_ir(state_update_ir),
.latched_jtag_ir(latched_jtag_ir)
);
JtagTapDRegs _dregs(
.tck(tck),
.trst(trst),
.tdi(tdi),
.tdo(tdo),
.state_test_logic_reset(state_test_logic_reset),
.state_capture_dr(state_capture_dr),
.state_shift_dr(state_shift_dr),
.state_shift_ir(state_shift_ir),
.latched_jtag_ir(latched_jtag_ir),
.debug_tdo(debug_tdo),
.bs_chain_tdo(debug_tdo),
.mbist_tdo(mbist_tdo),
.insn_tdo(insn_tdo),
.jdpacc_tdo(jdpacc_tdo),
.cdpacc_tdo(cdpacc_tdo),
.insn_extest_select(insn_extest_select),
.insn_sample_preload_select(insn_sample_preload_select),
.insn_idcode_select(insn_idcode_select),
.insn_mbist_select(insn_mbist_select),
.insn_debug_select(insn_debug_select),
.insn_bypass_select(insn_bypass_select),
.insn_jdpacc_select(insn_jdpacc_select),
.insn_cdpacc_select(insn_cdpacc_select)
);
endmoduleModule "JtagTapDRegs", blocks/JtagCoreDbg/rtl/JtagTapDRegs.sv
Parameters:
- IDCODE_VALUE
- INSN_WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| tck | input | wire | |
| trst | input | wire | |
| tdi | input | wire | |
| state_test_logic_reset | input | wire | |
| state_capture_dr | input | wire | |
| state_shift_dr | input | wire | |
| state_shift_ir | input | wire | |
| latched_jtag_ir | input | wire [INSN_WIDTH-1:0] | TDI signals from other modules Data Registers |
| debug_tdo | input | wire | |
| bs_chain_tdo | input | wire | |
| mbist_tdo | input | wire | |
| insn_tdo | input | wire | |
| jdpacc_tdo | input | wire | |
| cdpacc_tdo | input | wire | |
| tdo | output | reg | 1-bit telling instruction type |
| insn_extest_select | output | reg | |
| insn_sample_preload_select | output | reg | |
| insn_idcode_select | output | reg | |
| insn_mbist_select | output | reg | |
| insn_debug_select | output | reg | |
| insn_bypass_select | output | reg | |
| insn_jdpacc_select | output | reg | |
| insn_cdpacc_select | output | reg |
JTAG TAP Data Registers and TDO MUX.
Author: Igor Lesik 2020
Source code:
module JtagTapDRegs #(
parameter IDCODE_VALUE=DEFAULT_IDCODE_VALUE,
parameter INSN_WIDTH=8
)(
input wire tck,
input wire trst,
input wire tdi,
input wire state_test_logic_reset,
input wire state_capture_dr,
input wire state_shift_dr,
input wire state_shift_ir,
input wire [INSN_WIDTH-1:0] latched_jtag_ir,
// TDI signals from other modules Data Registers
input wire debug_tdo,
input wire bs_chain_tdo,
input wire mbist_tdo,
input wire insn_tdo,
input wire jdpacc_tdo,
input wire cdpacc_tdo,
output reg tdo,
// 1-bit telling instruction type
output reg insn_extest_select,
output reg insn_sample_preload_select,
output reg insn_idcode_select,
output reg insn_mbist_select,
output reg insn_debug_select,
output reg insn_bypass_select,
output reg insn_jdpacc_select,
output reg insn_cdpacc_select
);
localparam INSN_EXTEST = 8'b0000_0000;
localparam INSN_SAMPLE_PRELOAD = 8'b0000_0001;
localparam INSN_IDCODE = 8'b0000_0010;
localparam INSN_DEBUG = 8'b0000_1000;
localparam INSN_MBIST = 8'b0000_1001;
localparam INSN_JDPACC = 8'b0000_0100;
localparam INSN_CDPACC = 8'b0000_0101;
localparam INSN_BYPASS = 8'b1111_1111; // all 1's required by the standard
wire idcode_tdo, bypass_tdo;
assign insn_extest_select = (latched_jtag_ir == INSN_EXTEST);
assign insn_sample_preload_select = (latched_jtag_ir == INSN_SAMPLE_PRELOAD);
assign insn_idcode_select = (latched_jtag_ir == INSN_IDCODE);
assign insn_mbist_select = (latched_jtag_ir == INSN_MBIST);
assign insn_debug_select = (latched_jtag_ir == INSN_DEBUG);
assign insn_bypass_select = (latched_jtag_ir == INSN_BYPASS);
assign insn_jdpacc_select = (latched_jtag_ir == INSN_JDPACC);
assign insn_cdpacc_select = (latched_jtag_ir == INSN_CDPACC);
// TDO is muxed/selected based on value of Instruction Register (IR).
reg tdo_mux;
// TDO changes state at negative edge of TCK
always @(negedge tck) begin
tdo = tdo_mux;
end
// MUX-ing TDOs of the Data Registers
always_comb begin
if (state_shift_ir)
tdo_mux = insn_tdo;
else begin
//$display("%t JTAG IR=%h", $time, latched_jtag_ir);
case (latched_jtag_ir)
INSN_IDCODE: tdo_mux = idcode_tdo;
INSN_DEBUG: tdo_mux = debug_tdo;
INSN_SAMPLE_PRELOAD: tdo_mux = bs_chain_tdo;
INSN_EXTEST: tdo_mux = bs_chain_tdo;
INSN_MBIST: tdo_mux = mbist_tdo;
INSN_JDPACC: tdo_mux = jdpacc_tdo;
INSN_CDPACC: tdo_mux = cdpacc_tdo;
INSN_BYPASS: tdo_mux = bypass_tdo;
default: tdo_mux = bypass_tdo;
endcase
end
end
// IDCODE Data Register
reg [31:0] idcode_reg;
always @(posedge tck)
begin
if (trst == 1)
idcode_reg <= IDCODE_VALUE; // IDCODE selected after reset
else if (state_test_logic_reset)
idcode_reg <= IDCODE_VALUE; // IDCODE selected after reset
else if (insn_idcode_select & state_capture_dr)
idcode_reg <= IDCODE_VALUE;
else if (insn_idcode_select & state_shift_dr) begin
idcode_reg <= {tdi, idcode_reg[31:1]};
//$display("JTAG TAP IDCODE Shift-DR %h", idcode_reg);
end
end
assign idcode_tdo = idcode_reg[0];
// BYPASS Data Register
reg bypass_reg; // 1-bit register
always @(posedge tck)
begin
if (trst == 1)
bypass_reg <= 1'b0;
else if (state_test_logic_reset == 1)
bypass_reg <= 1'b0;
else if (insn_bypass_select & state_capture_dr)
bypass_reg <= 1'b0;
else if (insn_bypass_select & state_shift_dr)
bypass_reg <= tdi;
end
assign bypass_tdo = bypass_reg;
endmoduleModule "JtagTapFsm", blocks/JtagCoreDbg/rtl/JtagTapFsm.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| tck | input | wire | |
| trst | input | wire | |
| tms | input | wire | |
| state | output | reg [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| tms_reset | output | reg | 5 consecutive TMS=1 causes reset |
| state_test_logic_reset | output | reg | |
| state_run_test_idle | output | reg | |
| state_select_dr_scan | output | reg | |
| state_capture_dr | output | reg | |
| state_shift_dr | output | reg | |
| state_exit1_dr | output | reg | |
| state_pause_dr | output | reg | |
| state_exit2_dr | output | reg | |
| state_update_dr | output | reg | |
| state_select_ir_scan | output | reg | |
| state_capture_ir | output | reg | |
| state_shift_ir | output | reg | |
| state_exit1_ir | output | reg | |
| state_pause_ir | output | reg | |
| state_exit2_ir | output | reg | |
| state_update_ir | output | reg |
JTAG TAP state machine. Author: Igor Lesik 2020

The state machine is simple, comprising two paths: DR path and IR path. The state machine progresses on the test clock (TCK) edge, with the value of the test mode select (TMS) pin controlling the behavior/transition.
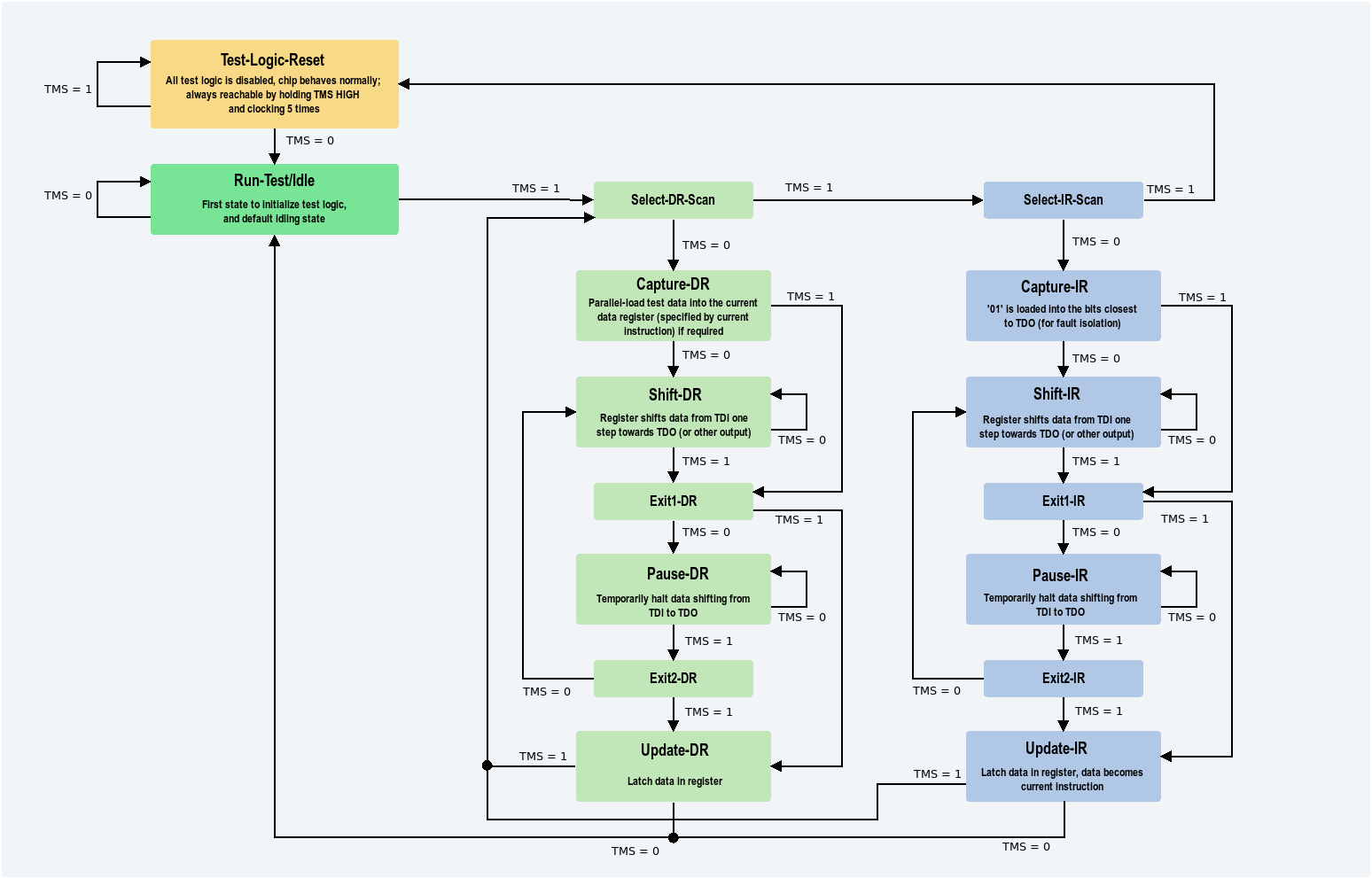
The Shift-DR and Shift-IR states are the main states for serial-loading data into either data registers or the instruction register. While the state machine is in one of these states, TMS is held LOW, until the shifting operation is complete. The Update-DR and Update-IR states latch the data into the registers, setting the data in the instruction register as the current instruction (and in doing so, setting the current data register for the next cycle).
Source code:
module JtagTapFsm #(
localparam WIDTH = JTAG_TAP_STATE_VAR_WIDTH
)(
input wire tck,
input wire trst,
input wire tms,
output reg [WIDTH-1:0] state,
output reg tms_reset, // 5 consecutive TMS=1 causes reset
output reg state_test_logic_reset,
output reg state_run_test_idle,
output reg state_select_dr_scan,
output reg state_capture_dr,
output reg state_shift_dr,
output reg state_exit1_dr,
output reg state_pause_dr,
output reg state_exit2_dr,
output reg state_update_dr,
output reg state_select_ir_scan,
output reg state_capture_ir,
output reg state_shift_ir,
output reg state_exit1_ir,
output reg state_pause_ir,
output reg state_exit2_ir,
output reg state_update_ir
);
assign state_test_logic_reset = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_TEST_LOGIC_RESET);
assign state_run_test_idle = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_RUN_TEST_IDLE);
assign state_select_dr_scan = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_SELECT_DR_SCAN);
assign state_capture_dr = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_CAPTURE_DR);
assign state_shift_dr = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_SHIFT_DR);
assign state_exit1_dr = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT1_DR);
assign state_pause_dr = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_PAUSE_DR);
assign state_exit2_dr = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT2_DR);
assign state_update_dr = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_UPDATE_DR);
assign state_select_ir_scan = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_SELECT_IR_SCAN);
assign state_capture_ir = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_CAPTURE_IR);
assign state_shift_ir = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_SHIFT_IR);
assign state_exit1_ir = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT1_IR);
assign state_pause_ir = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_PAUSE_IR);
assign state_exit2_ir = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT2_IR);
assign state_update_ir = (state == JTAG_TAP_STATE_UPDATE_IR);
reg [WIDTH-1:0] next_state;
// A transition between the states only occurs on the rising edge of TCK.
always @(posedge tck) begin
if (trst == 1 || tms_reset)
state <= JTAG_TAP_STATE_TEST_LOGIC_RESET;
else begin
state <= next_state;
//if (state != next_state)
// $display("JTAG TAP FSIM state %h -> %h", state, next_state);
end
end
// Determination of next state
always_comb
begin
case (state)
JTAG_TAP_STATE_TEST_LOGIC_RESET: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_TEST_LOGIC_RESET:JTAG_TAP_STATE_RUN_TEST_IDLE;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_RUN_TEST_IDLE: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_SELECT_DR_SCAN:JTAG_TAP_STATE_RUN_TEST_IDLE;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_SELECT_DR_SCAN: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_SELECT_IR_SCAN:JTAG_TAP_STATE_CAPTURE_DR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_CAPTURE_DR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT1_DR:JTAG_TAP_STATE_SHIFT_DR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_SHIFT_DR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT1_DR:JTAG_TAP_STATE_SHIFT_DR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT1_DR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_UPDATE_DR:JTAG_TAP_STATE_PAUSE_DR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_PAUSE_DR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT2_DR:JTAG_TAP_STATE_PAUSE_DR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT2_DR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_UPDATE_DR:JTAG_TAP_STATE_SHIFT_DR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_UPDATE_DR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_SELECT_DR_SCAN:JTAG_TAP_STATE_RUN_TEST_IDLE;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_SELECT_IR_SCAN: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_TEST_LOGIC_RESET:JTAG_TAP_STATE_CAPTURE_IR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_CAPTURE_IR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT1_IR:JTAG_TAP_STATE_SHIFT_IR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_SHIFT_IR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT1_IR:JTAG_TAP_STATE_SHIFT_IR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT1_IR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_UPDATE_IR:JTAG_TAP_STATE_PAUSE_IR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_PAUSE_IR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT2_IR:JTAG_TAP_STATE_PAUSE_IR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_EXIT2_IR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_UPDATE_IR:JTAG_TAP_STATE_SHIFT_IR;
end
JTAG_TAP_STATE_UPDATE_IR: begin
next_state = (tms)? JTAG_TAP_STATE_SELECT_DR_SCAN:JTAG_TAP_STATE_RUN_TEST_IDLE;
end
default: begin // can't actually happen
next_state = JTAG_TAP_STATE_TEST_LOGIC_RESET;
end
endcase
//$display("JTAG TAP FSIM state=%h", next_state);
end
// 5 consecutive TMS=1 causes 5 FSM transitions terminating in RESET state;
// here we duplicate "5 TMS->RESET" in case FSM gets broken somehow (unlikely),
// perhaps we should remove this code.
reg tms_q1, tms_q2, tms_q3, tms_q4;
assign tms_reset = tms & tms_q1 & tms_q2 & tms_q3 & tms_q4;
always @(posedge tck) begin
tms_q1 <= tms;
tms_q2 <= tms_q1;
tms_q3 <= tms_q2;
tms_q4 <= tms_q3;
end
endmoduleModule "JtagTapInsnReg", blocks/JtagCoreDbg/rtl/JtagTapInsnReg.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
- INSN_IDCODE
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| tck | input | wire | |
| trst | input | wire | |
| tdi | input | wire | |
| state_test_logic_reset | input | wire | |
| state_capture_ir | input | wire | |
| state_shift_ir | input | wire | |
| state_update_ir | input | wire | |
| insn_tdo | output | reg | |
| latched_jtag_ir | output | reg [WIDTH-1:0] | Insn Reg latched on negedge of TCK |
JTAG TAP Instruction Register.
Author: Igor Lesik 2020
Most JTAG instructions can broadly be described as connecting different data registers to the TDI/TDO path. The BYPASS instruction connects TDI directly to TDO through a 1-bit shift register, the IDCODE instruction connects the identification code register to TDO, the EXTEST, INTEST, SAMPLE, PRELOAD instructions all connect the boundary-scan register (BSR) data register to TDI and TDO, and so on.
Source code:
module JtagTapInsnReg #(
parameter WIDTH=8,
parameter INSN_IDCODE=8'b0000_0010
)(
input wire tck,
input wire trst,
input wire tdi,
input wire state_test_logic_reset,
input wire state_capture_ir,
input wire state_shift_ir,
input wire state_update_ir,
output reg insn_tdo,
output reg [WIDTH-1:0] latched_jtag_ir // Insn Reg latched on negedge of TCK
);
reg [WIDTH-1:0] jtag_ir; // Instruction register
//reg [WIDTH-1:0] latched_jtag_ir; // Insn Reg latched on negedge of TCK
always @(posedge tck) begin
if (trst == 1)
jtag_ir <= {WIDTH{1'b0}};
else if (state_test_logic_reset == 1)
jtag_ir <= {WIDTH{1'b0}};
else if (state_capture_ir)
jtag_ir <= 8'b1111_0101; // This value is fixed for easier fault detection; TODO ???
else if (state_shift_ir)
jtag_ir <= {tdi, jtag_ir[WIDTH-1:1]};
end
assign insn_tdo = jtag_ir[0];
always @(negedge tck) begin
if (trst== 1)
latched_jtag_ir <= INSN_IDCODE;
else if (state_test_logic_reset)
latched_jtag_ir <= INSN_IDCODE;
else if (state_update_ir)
latched_jtag_ir <= jtag_ir;
end
endmoduleModule "PrgCounter", blocks/PrgCounter/rtl/PrgCounter.sv
Parameters:
- ADDR_WIDTH
- INSN_SIZE
- localparam
- localparam
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| clk | input | wire | |
| rst | input | ||
| rst_addr | input | ||
| pc_addr | output | reg [ADDR_WIDTH-1:ADDR_OFS] | |
| bit | input | ||
| ADDR_WIDTH | input | ||
| 1 | input | ||
| ADDR_OFS | input | ||
| current_pc | input |
Program Counter.
Author: Igor Lesik 2020 Copyright: Igor Lesik 2020
Assumes RISC style fixed instruction word size.
Source code:
module PrgCounter #(
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 32,
parameter INSN_SIZE = 4,
localparam INSN_WIDTH = INSN_SIZE * 8,
localparam ADDR_OFS = (INSN_SIZE <= 1)? 0 :
(INSN_SIZE <= 2)? 1 :
(INSN_SIZE <= 4)? 2 :
(INSN_SIZE <= 8)? 3 :
(INSN_SIZE <=16)? 4 : -1
)(
input wire clk,
input wire rst,
input wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:ADDR_OFS] rst_addr,
output reg [ADDR_WIDTH-1:ADDR_OFS] pc_addr
);
reg rst_delay1;
always @ (posedge clk)
begin
pc_addr <= next_pc(pc_addr, rst_delay1, rst_addr);
rst_delay1 <= rst;
end
// Calculate next PC.
//
function bit [ADDR_WIDTH-1:ADDR_OFS] next_pc(
input bit [ADDR_WIDTH-1:ADDR_OFS] current_pc,
input bit rst,
input bit [ADDR_WIDTH-1:ADDR_OFS] rst_addr
);
if (rst) begin
next_pc = rst_addr;
end
else begin
next_pc = current_pc + 1;
end
//$display("PC: %x, rst: %d", next_pc, rst);
endfunction
endmoduleModule "ShiftReg", blocks/ShiftReg/rtl/ShiftReg.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| clk | input | wire | |
| srl_prl | input | wire | |
| srl_in | input | wire | |
| prl_in | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| srl_out | output | wire | |
| prl_out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
@file @brief Shift register @author Igor Lesik 2020
parallel load + shift reg Nth bit | mux ^ | +----+ +---------+ | | | | | | | +-------+ 0 | | DFF | | | | | | | | +------+ +---+---> +---------+ 1 | | | to next prev stage | | | | stage output +-+--+ +---------+ | + serial/parallel selector
Source code:
module ShiftReg #(
parameter WIDTH = 8
)(
input wire clk,
input wire srl_prl,
input wire srl_in,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] prl_in,
output wire srl_out,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] prl_out
);
wire [WIDTH-1:0] ff_in;
wire [WIDTH-1:0] srls_in;
assign srl_out = prl_out[WIDTH-1];
assign srls_in[0] = srl_in;
assign srls_in[WIDTH-1:1] = prl_out[WIDTH-2:0];
Mux2#(.WIDTH(WIDTH)) mux_(
.in1(prl_in),
.in2(srls_in),
.sel(srl_prl),
.out(ff_in)
);
Dff#(.WIDTH(WIDTH)) ff_(
.clk(clk),
.in(ff_in),
.out(prl_out)
);
endmoduleModule "SimRAM", blocks/SimRAM/rtl/SimRAM.sv
Parameters:
- DATA_SIZE
- 1
- 2
- 4
- ADDR_WIDTH
- MEM_SIZE
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| clk | input | wire | |
| rd_en | input | wire | |
| rd_addr | input | wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| wr_en | input | wire | |
| wr_addr | input | wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| wr_data | input | wire [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| rd_data | output | reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] |
Verilog simulation RAM model.
Author: Igor Lesik 2013-2020
Source code:
module SimRAM #(
parameter DATA_SIZE = 1, // 1-byte, 2-16bits, 4-32bits word
localparam DATA_WIDTH = 8 * DATA_SIZE,
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 8,
parameter MEM_SIZE = 2**ADDR_WIDTH
)(
input wire clk,
input wire rd_en,
input wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] rd_addr,
input wire wr_en,
input wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] wr_addr,
input wire [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] wr_data,
output reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] rd_data
);
reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] ram [MEM_SIZE];
localparam VLOG_HEX_FORMAT = 0;
localparam VLOG_BIN_FORMAT = 1;
//TODO localparam SREC_FORMAT = 2;
// Load memory contents from a file.
//
function int load(string filename, int format);
if (format == VLOG_HEX_FORMAT)
$readmemh(filename, ram);
else if (format == VLOG_BIN_FORMAT)
$readmemb(filename, ram);
else
return 0;
return 1;
endfunction
always @ (posedge clk)
begin
if (wr_en) begin
ram[integer'(wr_addr)] <= wr_data;
end
if (rd_en) begin
//$display("ROM[%h]=%h", integer'(addr)+i, rom[integer'(addr)+i]);
rd_data <= ram[integer'(rd_addr)];
if (wr_en && rd_addr == wr_addr) begin
assert(0);//FIXME
end
end
end
endmoduleModule "SimROM", blocks/SimROM/rtl/SimROM.sv
Parameters:
- DATA_SIZE
- 1
- 2
- 4
- ADDR_WIDTH
- MEM_SIZE
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| clk | input | wire | |
| addr | input | wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] | |
| data | output | reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] |
Verilog simulation ROM model.
Author: Igor Lesik 2013-2020
Verilog binary format example:
@003 00000011 00000100 @005 00000101
Verilog hex format example:
@003 3 4
Source code:
module SimROM #(
parameter DATA_SIZE = 1, // 1-byte, 2-16bits, 4-32bits word
localparam DATA_WIDTH = 8 * DATA_SIZE,
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 8,
parameter MEM_SIZE = 2**ADDR_WIDTH
)(
input wire clk,
input wire [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] addr,
output reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] data
);
reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] rom [MEM_SIZE];
localparam VLOG_HEX_FORMAT = 0;
localparam VLOG_BIN_FORMAT = 1;
//TODO localparam SREC_FORMAT = 2;
function int load(string filename, int format);
if (format == VLOG_HEX_FORMAT)
$readmemh(filename, rom);
else if (format == VLOG_BIN_FORMAT)
$readmemb(filename, rom);
else
return 0;
return 1;
endfunction
always @ (posedge clk)
begin
//$display("ROM[%h]=%h", integer'(addr)+i, rom[integer'(addr)+i]);
data <= rom[integer'(addr)];
end
endmoduleModule "INV", lib/gates/builtin/INV.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | out = ~in |
Inverter.
Wrapper around Inv.
Source code:
module INV #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out // out = ~in
);
Inv#(WIDTH) inv_(.in(in), .out(out));
endmoduleModule "Inv", lib/gates/builtin/Inv.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | out = ~in |
Inverter.
Source code:
module Inv #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out // out = ~in
);
not /*(strength)*/ /*#(2 delays)*/ not_(out, in);
endmoduleModule "MUX2", lib/gates/builtin/MUX2.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| sel | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
2:1 Multiplexer
Source code:
module MUX2 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
input wire sel,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
Mux2#(WIDTH) mux2_(.in1(in1), .in2(in2), .sel(sel), .out(out));
endmoduleModule "Mux2", lib/gates/builtin/Mux2.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| sel | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
Multiplexer made with NAND
Author: Igor Lesik 2020.
+------+
| |
in1 +-----------+ NAND |
| |o+-+ +------+
sel +-----+-----+ | | | |
| | | | | |
| +------+ +----+ NAND |
| | |o+----+ out
| +------+ +----+ |
| | | | | |
+---+o| NAND | | | |
| |o+-+ +------+
in2 +-----------+ |
| |
+------+
Source code:
module Mux2 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
input wire sel,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
wire [WIDTH-1:0] o1, o2;
NAND2#(WIDTH) nand1_(.out(o1), .in1(in1), .in2({WIDTH{sel}}));
NAND2#(WIDTH) nand2_(.out(o2), .in1(in2), .in2({WIDTH{~sel}}));
NAND2#(WIDTH) nand3_(.out(out), .in1(o1), .in2(o2));
endmoduleModule "NAND2", lib/gates/builtin/NAND2.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
2-input NAND.
Source code:
module NAND2 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
NAnd2#(WIDTH) nand_(.in1(in1), .in2(in2), .out(out));
endmoduleModule "NAnd2", lib/gates/builtin/NAnd2.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
2-input NAND.
Source code:
module NAnd2 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
nand /*(strength)*/ /*#(3 delays)*/ nand_(out, in1, in2);
endmoduleModule "AND2", lib/gates/cmos/AND2.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire | |
| in2 | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire |
2-input AND.
Source code:
module AND2 (
input wire in1,
input wire in2,
output wire out
);
wire nand_output;
NAnd2 nand2_(.in1(in1), .in2(in2), .out(nand_output));
Inv inv_ (.in(nand_output), .out(out));
endmoduleModule "INV", lib/gates/cmos/INV.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | out = ~in |
Inverter.
Uses Inv.
Source code:
module INV #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out // out = ~in
);
genvar i;
generate
for (i = 0; i < WIDTH; i = i + 1) begin
Inv inv_(.in(in[i]), .out(out[i]));
end
endgenerate
endmoduleModule "Inv", lib/gates/cmos/Inv.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire | out = ~in |
CMOS Inverter gate.
Use Verilog keywords pmos and nmos to define 2 transistors:
pmos p1 (out, vdd, in); // out = HI(vdd) if in is LO
nmos n1 (out, gnd, in); // out = LO(gnd) if in is HI
See book by Yamin Li, Computer principles and design in Verilog HDL.
+-------+-----+ vdd
|
+ |
+ +---+
+----o| | p1
| + +---+
| + |
| |
+----+ +------+
| |
| + |
| + +---+
+-----+ | n1
+ +---+
+ |
|
|
+---------+----+ gnd
Source code:
module Inv (
input wire in,
output wire out // out = ~in
);
supply1 vdd; // logic 1 (power)
supply0 gnd; // logic 0 (ground)
// pmos (drain, source, gate);
pmos p1 (out, vdd, in);
// nmos (drain, source, gate);
nmos n1 (out, gnd, in);
endmoduleModule "MUX2", lib/gates/cmos/MUX2.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| sel | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
2:1 Multiplexer.
Source code:
module MUX2 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
input wire sel,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
genvar i;
generate
for (i = 0; i < WIDTH; i = i + 1) begin
Mux2 mux2_(.in1(in1[i]), .in2(in2[i]), .sel(sel), .out(out[i]));
end
endgenerate
endmoduleModule "Mux2", lib/gates/cmos/Mux2.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire | |
| in2 | input | wire | |
| sel | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire |
2:1 Multiplexer.
---------+-------------+------ vdd
| |
in1 +--o| p1 in2 +--o| p3
| | pmos is open when gate 0
| |
~sel +--o| p2 sel +--o| p4
| |
+-------------+---------INV----->
| |
sel +---| n1 ~sel +--o| n3
| | nmos is open when gate 1
| |
in1 +---| n2 in2 +---| n4
| |
| |
--+-------------+------ gnd
Source code:
module Mux2 (
input wire in1,
input wire in2,
input wire sel,
output wire out
);
supply1 vdd;
supply0 gnd;
wire nsel;
INV inv_sel_(.in(sel), .out(nsel));
wire o;
INV inv_out_(.in(o), .out(out));
wire p1_p2, p3_p4, n1_n2, n3_n4;
// pmos drain source gate
pmos p1(p1_p2, vdd, in1);
pmos p2(o, p1_p2, nsel);
pmos p3(p3_p4, vdd, in2);
pmos p4(o, p3_p4, sel);
// nmos drain source gate
nmos n1(o, n1_n2, sel);
nmos n2(n1_n2, gnd, in1);
nmos n3(o, n3_n4, nsel);
nmos n4(n3_n4, gnd, in2);
endmoduleModule "NAND2", lib/gates/cmos/NAND2.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
2-input NAND.
Uses NAnd2
Source code:
module NAND2 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
genvar i;
generate
for (i = 0; i < WIDTH; i = i + 1) begin
NAnd2 nand2_(.in1(in1[i]), .in2(in2[i]), .out(out[i]));
end
endgenerate
endmoduleModule "NAnd2", lib/gates/cmos/NAnd2.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire | |
| in2 | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire |
2-input NAND.
---------+-------------+------ vdd
| |
+--o| p1 +--o| p2
| | | |
| +-------------+------ out
| | |
in1 -+-----------------| n1
| |
in2 ---------------+---| n2
|
--------+------ gnd
Source code:
module NAnd2 (
input wire in1,
input wire in2,
output wire out
);
supply1 vdd;
supply0 gnd;
wire w_n; // connects 2 nmos transistors
// pmos drain source gate
pmos p1(out, vdd, in1);
pmos p2(out, vdd, in2);
// nmos drain source gate
nmos n1(out, w_n, in1);
nmos n2(w_n, gnd, in2);
endmoduleModule "NOR2", lib/gates/cmos/NOR2.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire | |
| in2 | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire |
2-input NOR
Wrapper around NOr2
Source code:
module NOR2 (
input wire in1,
input wire in2,
output wire out
);
NOr2 nor2_(.in1(in1), .in2(in2), .out(out));
endmoduleModule "NOr2", lib/gates/cmos/NOr2.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire | |
| in2 | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire |
2-input NOR
-------------+------ vdd
|
in1 ---+--------------o| p1
| |
in2 -------------+----o| p2
| | |
| +------------+------ out
| | | |
+--| n1 +-----| n2
| |
---+------------+---- gnd
Source code:
module NOr2 (
input wire in1,
input wire in2,
output wire out
);
supply1 vdd;
supply0 gnd;
wire w_p; // connects 2 pmos transistors
// nmos drain source gate
pmos n1(out, gnd, in1);
pmos n2(out, gnd, in2);
// pmos drain source gate
pmos p1(w_p, vdd, in1);
pmos p2(out, w_p, in2);
endmoduleModule "AOI22", lib/gates/generic/AOI22.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | to be AND-ed with in2 |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | to be AND-ed with in1 |
| in3 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | to be AND-ed with in4 |
| in4 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | to be AND-ed with in3 |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | NOR the results of two ANDs |
Complex gate And-Or-Invertor.
in1 ----------+--\
AND +----+
in2 ----------+--/| |
|NOR |o-----
in3 ----------+--\| |
AND +----+
in4 ----------+--/
Source code:
module AOI22 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1, // to be AND-ed with in2
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2, // to be AND-ed with in1
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in3, // to be AND-ed with in4
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in4, // to be AND-ed with in3
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out // NOR the results of two ANDs
);
assign out = ~((in1 & in2) | (in3 & in4));
endmoduleModule "Dff", lib/gates/generic/Dff.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| clk | input | wire | |
| in | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| out | output | reg [WIDTH-1:0] |
@file @brief Rising edge triggered D Flip Flop @author Igor Lesik @copyright Igor Lesik 2014
Source code:
module Dff #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire clk,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in,
output reg [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
always_ff @(posedge clk)
out[WIDTH-1:0] <= in[WIDTH-1:0];
`ifdef DFF_RANDOMIZE_INITIAL_VALUE
initial begin
out = $urandom_range(2**WIDTH - 1, 0);
end
`endif
endmoduleModule "INV", lib/gates/generic/INV.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | to be inverted |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | out is inverted in |
Inverter.
Source code:
module INV #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in, // to be inverted
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out // out is inverted in
);
assign out = ~in;
endmoduleModule "MUX2", lib/gates/generic/MUX2.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| sel | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
2:1 Multiplexer
Source code:
module MUX2 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
input wire sel,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
Mux2#(WIDTH) mux2_(.in1(in1), .in2(in2), .sel(sel), .out(out));
endmoduleModule "MUX4", lib/gates/generic/MUX4.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in3 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in4 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| sel | input | wire [1:0] | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
4:1 Multiplexer
Source code:
module MUX4 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in3,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in4,
input wire [1:0] sel,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
Mux4#(WIDTH) mux4_(.in1, .in2, .in3, .in4, .sel, .out);
endmoduleModule "Mux2", lib/gates/generic/Mux2.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| sel | input | wire | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
2:1 Multiplexer.
Author: Igor Lesik 2014.
+-----+
in1 ------| 1 |
| MUX |--- out
in2 ------| 0 |
+--+--+
sel |
Source code:
module Mux2 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
input wire sel,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
assign out = (sel == 1) ? in1 : in2;
endmoduleModule "Mux4", lib/gates/generic/Mux4.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in3 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in4 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| sel | input | wire [1:0] | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
4:1 Multiplexer Author: Igor Lesik 2014
Source code:
module Mux4 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in3,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in4,
input wire [1:0] sel,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
assign out = (sel == 0) ? in1 :
(sel == 1) ? in2 :
(sel == 2) ? in3 : in4;
/*
assign Z = (~S1 & ~S0 & I0)
| (~S1 & S0 & I1)
| ( S1 & ~S0 & I2)
| ( S1 & S0 & I3);*/
endmoduleModule "NAND2", lib/gates/generic/NAND2.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| out | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
2-input NAND.
Source code:
module NAND2 #(
parameter WIDTH = 1
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] out
);
assign out = ~(in1 & in2);
endmoduleModule "FullAdderAOI", lib/parts/FullAdderAOI.sv
Parameters:
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire | |
| in2 | input | wire | |
| ci | input | wire | carry in |
| sum | output | wire | |
| co | output | wire | carry out |
Full Adder using And-Or-Invert (AOI) logic.
Author: Igor Lesik 2020.
AOI logic is a technique of using equivalent Boolean logic expressions to reduce the number of gates required for a particular expression. This, in turn, reduces capacitance and consequently propagation times.
For this design, AOI logic has been applied to the calculation of the Sum bit:
Sumₖ = Aₖ ⊕ Bₖ ⊕ Cₖ = (Aₖ + Bₖ + Cₖ)~Cₖ₊₁ + AₖBₖCₖ
where Cₖ₊₁ = AₖBₖ + Cₖ(Aₖ + Bₖ)
Instead of using two XOR gates to implement the Sum bit, the circuit takes advantage of the fact that ~Cₖ₊₁ already computed and uses fewer gates to calculate the rest of the expression.
Source code:
module FullAdderAOI (
input wire in1,
input wire in2,
input wire ci, // carry in
output wire sum,
output wire co // carry out
);
wire co_n, sum_n;
assign co = ~co_n;
assign sum = ~sum_n;
AOI22 aoi_co_(.out(co_n), .in1(in1|in2), .in2(ci), .in3(in1), .in4(in2));
AOI22 aoi_sum_(.out(sum_n), .in1(co_n), .in2(in1|in2|ci), .in3(in1), .in4(in2 & ci));
endmoduleModule "RippleCarryAdder", lib/parts/RippleCarryAdder.sv
Parameters:
- WIDTH
Ports:
| Name | Direction | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| in1 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| in2 | input | wire [WIDTH-1:0] | |
| ci | input | wire | |
| co | output | wire | |
| sum | output | wire [WIDTH-1:0] |
- Fast Ripple-Carry Adders in Standard-Cell CMOS VLSI -CMOS Binary Full Adder, A Survey of Possible Implementations
Source code:
module RippleCarryAdder #(
parameter WIDTH = 64
)(
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in1,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] in2,
input wire ci,
output wire co,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] sum
);
/* verilator lint_off UNOPTFLAT */
wire [WIDTH:0] carry;
/* verilator lint_on UNOPTFLAT */
assign carry[0] = ci;
assign co = carry[WIDTH];
genvar i;
generate
for (i = 0; i < WIDTH; i++) begin : fa_gen
FullAdderAOI fa_(
.in1(in1[i]),
.in2(in2[i]),
.ci (carry[i]),
.sum(sum[i]),
.co (carry[i+1])
);
end
endgenerate
endmodule